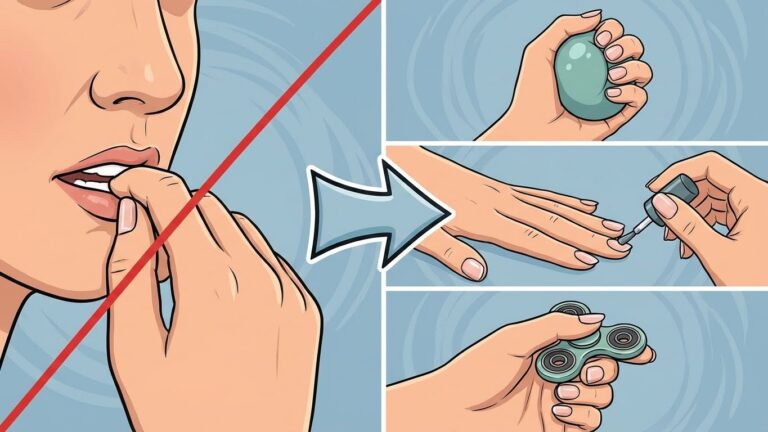
Nail biting is a common habit many people struggle to stop. It can make nails look unhealthy and even cause lasting damage to fingers, teeth, and gums. While breaking this habit isn’t always easy, there are clear steps anyone can take to reduce or stop nail biting for good.
The most effective way to avoid biting nails is by using a mix of behavioral techniques, keeping the hands busy, and understanding the reasons behind the habit. Identifying when and why nail biting happens helps create better strategies to fight it. Simple tactics like applying bitter nail polish or finding other ways to reduce stress and boredom often lead to lasting results.
Changing a habit takes time and patience. Using practical methods and sometimes seeking professional support can help maintain progress. Nail biting can be controlled with the right approach and commitment to healthier habits.
Key Takeaways
- Nail biting can cause physical damage and should be addressed early.
- Knowing your triggers helps you create effective ways to stop.
- Consistency and sometimes help from experts improve success.
Understanding Nail Biting
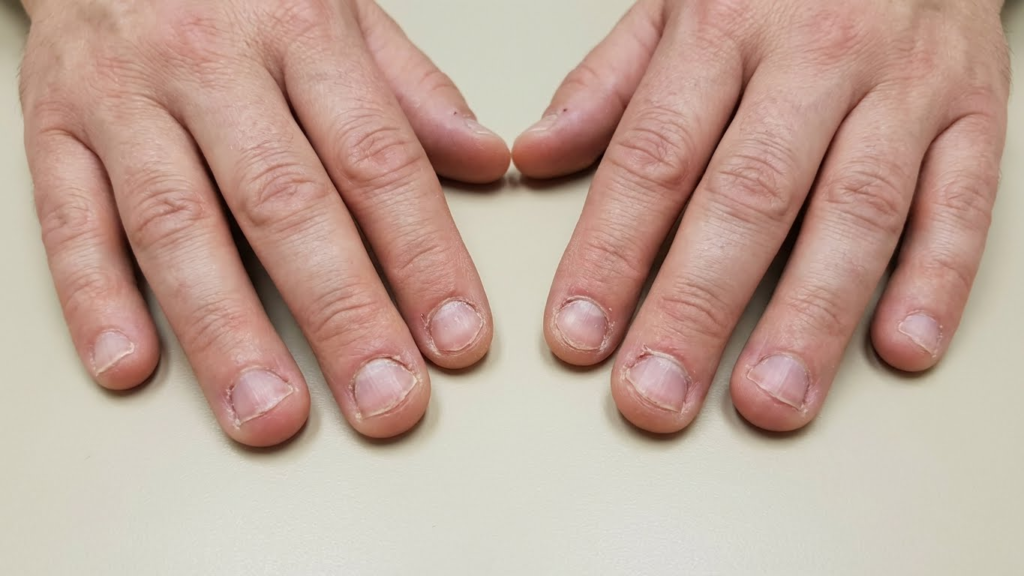
Nail biting is more than just a simple habit. It often happens because of specific feelings or situations and can affect both physical health and appearance. Recognizing what leads to nail biting and the effects it has can help in finding better ways to stop.
What Causes Nail Biting
Nail biting is usually a response to emotions or stress. Many people bite their nails when they feel anxious, bored, or stressed. It can also be part of a group of behaviors called body-focused repetitive behaviors (BFRBs), which include things like skin picking or hair pulling. These actions are often automatic and happen without the person realizing it.
Some individuals pick up nail biting in childhood, and it can continue into adulthood if not addressed. In some cases, underlying mental health issues like anxiety or obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) may make nail biting harder to stop. It is not just a bad habit but a behavior tied to how the brain manages stress or distraction.
Common Triggers for Nail Biting

Many triggers can cause someone to bite their nails. Stress and anxiety are the most common reasons. People often bite when they face pressure at work or school. Boredom can also lead to nail biting, as the hands seek something to do.
Certain emotional situations especially increase the urge to bite. For example, feeling nervous before a test or during an argument can raise the impulse. Some individuals bite their nails unconsciously during activities like watching TV or reading.
Identifying these triggers is key to controlling the habit. Keeping hands busy with a fidget toy or stress ball, or using other distractions, can reduce the chances of biting.
Impact of Nail Biting on Health
Nail biting can cause damage beyond just the nails. It makes the nails look uneven and unattractive. Repeated biting can lead to infections around the nails, due to bacteria entering small cuts or broken skin.
Nail biting can also affect teeth. Constant biting puts pressure on teeth and gums, which may cause dental problems like chipped teeth or gum injury. In severe cases, the habit could affect how teeth align.
Additionally, frequent nail biting increases the risk of ingrown nails and other nail disorders. Taking care of nails and avoiding biting can protect both appearance and overall health.
Identifying Your Nail Biting Patterns
Nail biting often happens without noticing. Identifying when and how it occurs helps to take control of the habit. Recognizing specific moments and tracking frequency can reveal the reasons behind it.
Recognizing When You Bite Your Nails
People tend to bite their nails during certain emotions or activities. Stress, boredom, or anxiety are common triggers. Nail biting might happen while watching TV, working, or even in social settings.
Physical signs show when someone bites their nails, such as:
| Sign | Description |
|---|---|
| Short or jagged nails | Nails appear uneven or bitten down |
| Red or inflamed skin | Skin around nails looks sore or irritated |
| Damaged cuticles | Cuticles may be torn or missing |
Noticing these signs helps to become aware of the habit. Awareness often slows down the urge to bite nails.
Tracking Nail Biting Habits
Tracking nail biting involves noting when, where, and why it happens. Keeping a simple journal or using a phone app can help.
A table to track nail biting might look like this:
| Time | Situation | Feeling or Trigger | Nail Biting Occurred (Yes/No) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morning | At breakfast | Stress | Yes |
| Afternoon | Working at desk | Boredom | No |
| Evening | Watching TV | Anxiety | Yes |
This information helps identify patterns and triggers. Once triggers are clear, specific strategies can be planned to avoid or manage them better.
Practical Strategies to Stop Nail Biting
Stopping nail biting takes a mix of simple habits, physical barriers, and sensory reminders. Each approach helps reduce the urge by either making nails less tempting or harder to bite.
Keeping Nails Trimmed and Maintained

Short nails reduce the surface area available to bite, which can lower the temptation. Keeping nails well-trimmed and clean makes biting less satisfying and minimizes damage.
Regular grooming also creates a sense of care and pride in one’s nails. When nails look neat, the urge to ruin them may decrease. Using a nail file to smooth rough edges can prevent accidental snagging that might trigger biting.
Maintaining nails with moisturizing creams keeps the skin healthy and reduces hangnails, which are common triggers. Overall, this routine supports nail health and lessens the physical reasons to bite.
Using Bitter-Tasting Nail Polishes
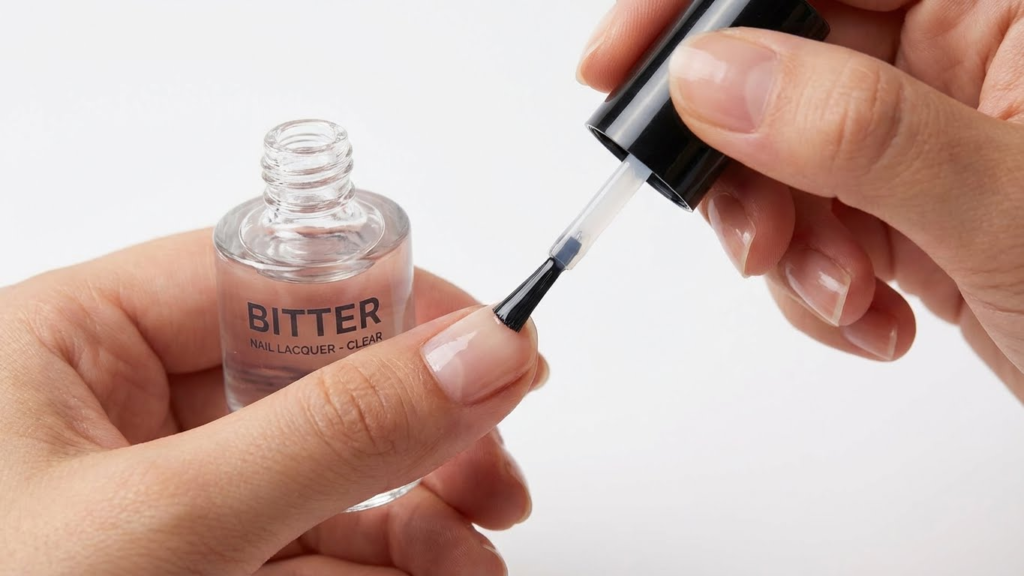

Applying bitter-tasting nail polish is a common deterrent. These special polishes have a harsh flavor that discourages nail biting by making the act unpleasant.
The bitterness acts as a quick reminder every time nails approach the mouth. This can interrupt automatic biting habits and build awareness of the behavior.
Some bitter polishes also contain vitamins and strengthening ingredients. This combination improves nail health while discouraging biting. Regular reapplication is important since the taste fades over time.
Covering Nails as a Deterrent
Physically covering nails can stop biting by blocking direct contact. Common methods include nail wraps, bandages, or gloves.
These covers serve as a tough reminder and make biting nails inconvenient or impossible. Colored nail wraps or decorative bandages may also add a visual incentive to keep nails intact.
Some use artificial nails or acrylics to provide a hard surface that reduces biting damage. While effective, these options require maintenance and may not suit everyone.
Using covers consistently during high-risk moments supports breaking the habit by changing the usual routine.
Behavioral Techniques for Lasting Change
Changing nail-biting requires active mental effort and new routines. It involves recognizing triggers, shifting habits, and managing emotions like stress. The methods below focus on replacing nail-biting with healthier behaviors and increasing self-control.
Habit Reversal Training
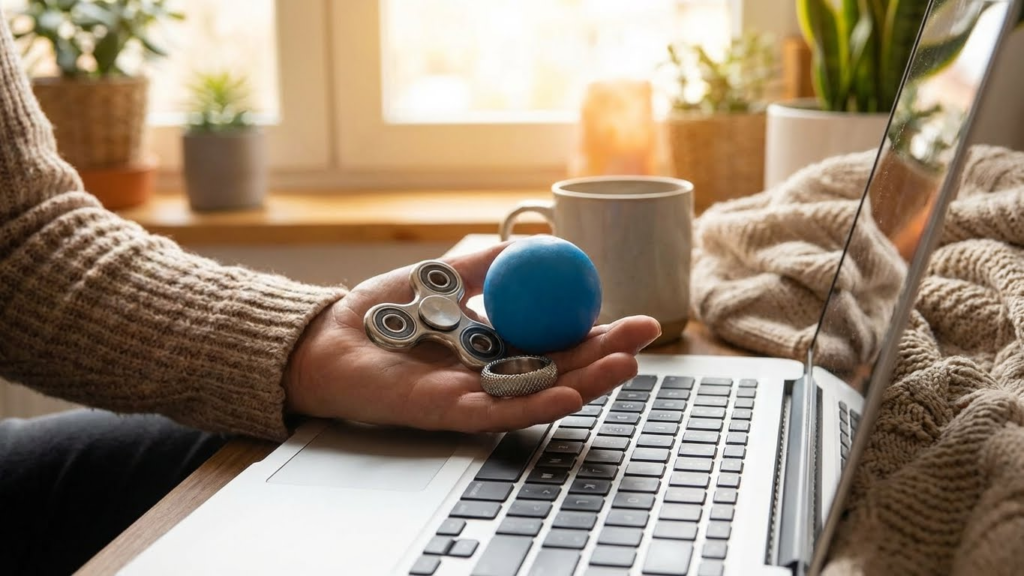

Habit Reversal Training (HRT) is a structured way to break nail-biting. It starts with awareness training, where individuals learn to notice when and why they bite their nails.
They then practice a competing response, which is a different, less harmful action done instead of biting. For example, clenching fists or squeezing a stress ball helps stop the urge.
HRT also involves motivational techniques like tracking progress and rewarding small wins. This keeps motivation high.
Regular practice and review are essential to solidify the new behavior. Over time, the competing response becomes automatic, reducing nail-biting episodes.
Mindfulness and Stress Management
Mindfulness helps people become more aware of their urges without acting on them. It teaches them to observe feelings and thoughts related to nail-biting without judgment.
Stress often triggers nail-biting, so managing stress is key. Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided meditation can reduce the anxiety that leads to biting.
Regular mindfulness practice strengthens self-control and reduces impulsive nail-biting. Keeping hands busy with hobbies or physical objects may also lower stress-driven urges.
Combining mindfulness with stress reduction creates a calmer state of mind, making it easier to resist nibbling nails.
Healthy Alternatives to Nail Biting
Finding ways to keep the hands busy and redirect the urge to bite nails can reduce the habit. Using objects or activities that engage the fingers helps channel energy away from biting.
Engaging Hands in Other Activities
One effective strategy is to give the hands a job that feels satisfying. Activities like knitting, drawing, or playing with stress balls offer a physical outlet. These prevent boredom and lower stress, two common triggers for nail biting.
When the hands are busy, the temptation weakens. For example, holding a pen or squeezing a soft ball uses fingers in a controlled way that replaces the biting motion. Keeping the hands occupied also builds good habits by breaking the cycle of nail biting.
| Activity | Benefits | Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Knitting or crochet | Focuses attention and hands | Start with simple projects |
| Drawing or doodling | Stimulates creativity | Use small sketchbooks |
| Squeezing stress ball | Reduces anxiety and stress | Choose soft, durable balls |
Using Fidget Tools
Fidget tools are small gadgets designed to keep fingers moving and distract from nail biting. These include spinners, cubes, and textured objects. Their use can calm nerves and provide a tactile substitute for nail biting.
Choosing a tool that fits comfortably in the hand is important. The tool should be quiet and portable, useful for work, school, or home. Regular use helps build new muscle memory that replaces the biting habit.
| Fidget Tool Type | Features | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Spinner | Smooth rolling motion | When needing distraction |
| Fidget cube | Multiple buttons and switches | For varied tactile input |
| Textured rings or bands | Soft texture for finger stimulation | Easy to wear and carry |
Seeking Professional Help
Some cases of nail biting are linked to deeper psychological issues like stress or anxiety. Knowing when to ask for help and understanding treatment options can make a significant difference for those struggling with this habit.
When to Consult a Therapist
People should consider talking to a therapist if nail biting starts to affect their daily life. This includes when it causes pain, infections, or social problems such as embarrassment or avoiding social events.
If nail biting is linked to anxiety, depression, or other mental health concerns, professional support is important. A therapist can help identify emotional triggers behind the habit. It is also useful when nail biting continues despite trying other methods to stop.
Treatment Options for Chronic Nail Biting
Therapists often use behavioral therapy to address nail biting. One common method is habit reversal training, which teaches a person to notice when they want to bite nails and replace it with a different action, such as squeezing a stress ball.
Other treatments focus on managing stress and anxiety that drive the behavior. This may include relaxation techniques, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), or medication if needed. Professional guidance helps maintain progress and prevent relapse by supporting long-term behavior change.
Maintaining Long-Term Progress
Stopping nail biting takes more than just willpower. Keeping track of progress and knowing how to respond to setbacks play a big role in lasting success.
Celebrating Milestones
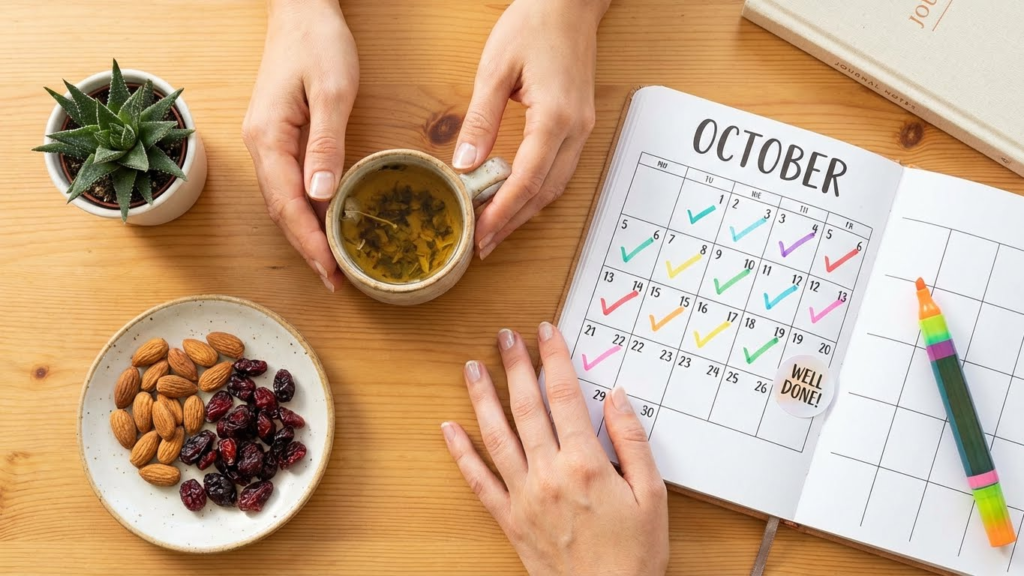

Recognizing small victories helps keep motivation high. Each day or week without biting nails is a step forward. Mark these moments with something rewarding, like a new nail care product or a small treat.
Tracking progress visually, such as using a calendar or app, can remind someone of how far they’ve come. Positive reinforcement encourages continued effort and helps build confidence over time.
Setting clear, achievable goals also matters. For example, aiming to avoid biting for one week before increasing the goal. Breaking the process into smaller steps makes progress feel manageable.
Handling Relapses
Relapses should not be seen as total failures. They are normal and can provide valuable lessons. It is important to identify triggers that cause nail biting, like stress or boredom, and find ways to manage them.
When a relapse happens, refocus quickly by restarting the commitment without guilt. Using physical reminders, such as wearing a rubber band on the wrist or keeping nails trimmed short, can discourage biting.
Support from friends or family helps maintain accountability. Talking openly about struggles can reduce embarrassment and provide encouragement during tough times.
Supporting Children Who Bite Their Nails
Helping children stop biting their nails involves patient approaches and cooperation from adults around them. Effective support combines calm techniques with teamwork at home, school, and other places the child spends time.
Gentle Interventions for Kids
Using gentle, positive methods encourages children to stop nail biting without causing shame. Parents can try offering small rewards when the child goes a certain time without biting. This helps build motivation.
Distractions like fidget toys or keeping their hands busy with crafts can reduce boredom, which often triggers nail biting. Calmly reminding the child and praising efforts, instead of scolding, makes the habit easier to change.
Sometimes, children bite their nails during stress or anxiety. Teaching simple breathing exercises or giving them a comfort object can lower this urge. Patience is key, as breaking the habit takes time.
Working with Schools and Caregivers
Teachers and caregivers can play a big role in supporting children who bite their nails. Sharing strategies used at home with school staff creates consistency.
It helps if adults at school gently redirect the child when they notice nail biting. They can offer alternatives, like squeezing a stress ball or holding a pencil, to keep hands busy.
Open communication between parents and caregivers ensures everyone understands the child’s needs. This team effort helps the child feel supported, reducing nail biting over time.
FAQS
Why do people bite their nails?
Nail biting often happens because of stress, boredom, or anxiety. It’s a way some people try to feel calm or in control. Sometimes, it can be linked to mental health issues.
Is nail biting harmful?
Yes. It can damage nails, gums, and teeth. It may also cause infections. Long-term nail biting can make nails look unhealthy and weak.
What are simple ways to stop nail biting?
People can try keeping their hands busy with things like stress balls. Using bitter-tasting nail polish helps discourage nail biting. Regular nail care, like trimming and moisturizing, also makes a difference.
When should someone seek help for nail biting?
If nail biting is frequent and hard to stop, and it affects daily life, it’s a good idea to talk to a healthcare provider. Therapy or behavioral treatments can offer support.
| Tip | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Keep nails trimmed | Less nail to bite reduces temptation |
| Use bitter nail polish | Taste discourages the habit |
| Find other activities | Keeps hands busy and distracted |
| Learn relaxation methods | Reduces anxiety and stress triggers |
Can nail biting be completely cured?
Many people can stop with practice and the right techniques. Success depends on consistency and sometimes professional help. It’s a habit that can be managed and reduced over time.
Conclusion
Stopping nail biting takes time and patience. It helps to replace the habit with healthier actions like using a stress ball or applying bitter-tasting nail polish. These tools can reduce the urge to bite and make hands less tempting.
Behavioral changes work best when combined with self-care. Relaxation techniques and managing anxiety support better control over nail biting. In some cases, professional help may be needed, especially if nail biting is linked to stress or other conditions.
Keeping nails clean and well-trimmed also prevents damage and discourages biting. Healthy nails are less likely to break and cause discomfort, which can reduce the desire to bite.
Key tips to avoid nail biting:
| Tip | Why it helps |
|---|---|
| Keep nails trimmed | Limits damage and temptation |
| Use bitter nail polish | Creates negative taste reminder |
| Find replacements (e.g., stress balls) | Occupies hands during urges |
| Practice relaxation methods | Reduces stress that triggers biting |
| Seek professional support if needed | Addresses underlying issues |
Building new habits is a gradual process. Consistency and awareness play important roles in success. With effort, it is possible to stop nail biting and maintain healthier nails over time.